CHAPTER 11 : BUILDING A CUSTOMER -CENTRIC ORGANIZATION – CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
-
CRM
enables an organization to:
·
Provide
better customer service
·
Make
call centers more efficient
·
Cross
sell products more effectively
·
Help
sales staff close deals faster
·
Simplify
marketing and sales processes
·
Discover
new customers
·
Increase
customer revenues
Recency,
Frequency, and Monetary Value
-
Organizations
can find their most valuable customers through “RFM” - Recency, Frequency, and
Monetary value
·
How
recently a customer purchased items (Recency)
·
How
frequently a customer purchased items (Frequency)
·
How
much a customer spends on each purchase (Monetary Value)
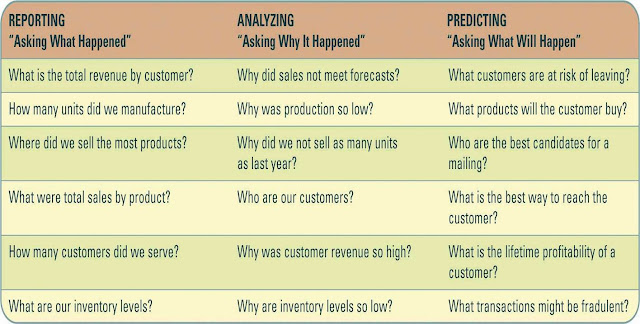
The
Evolution of CRM
-
CRM
reporting technology – help
organizations identify their customers across other applications
-
CRM
analysis technologies – help
organization segment their customers into categories such as best and worst
customers
-
CRM
predicting technologies – help
organizations make predictions regarding customer behaviour such as which
customers are at risk of leaving
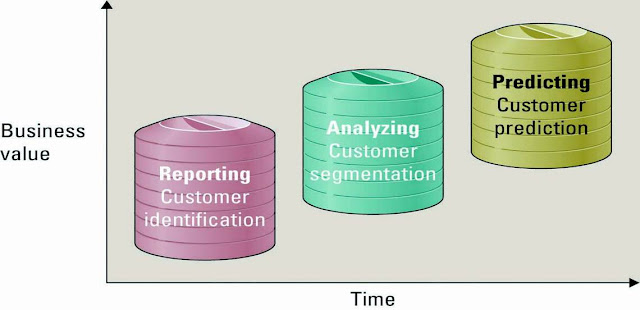
Three phases in the evolution of CRM
include reporting, analysing, and predicting
The
Ugly Side of CRM

Customer
Relationship Management’s Explosive Growth
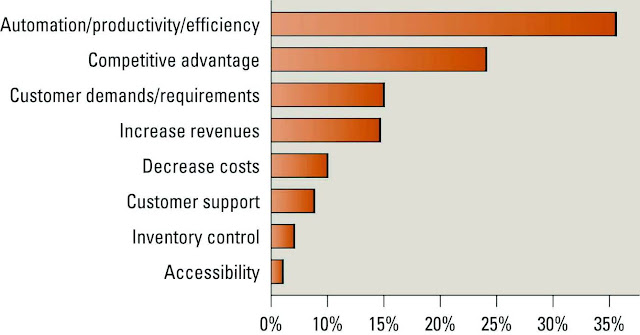
CRM Business Drivers
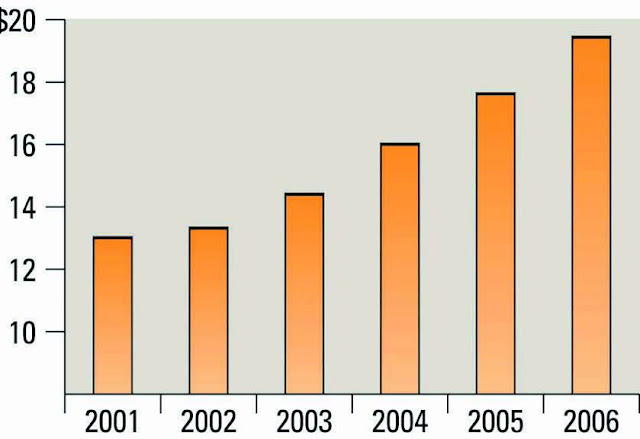
Forecasts for CRM Spending (in
billions)
Using
Analytical CRM to Enhance Decisions
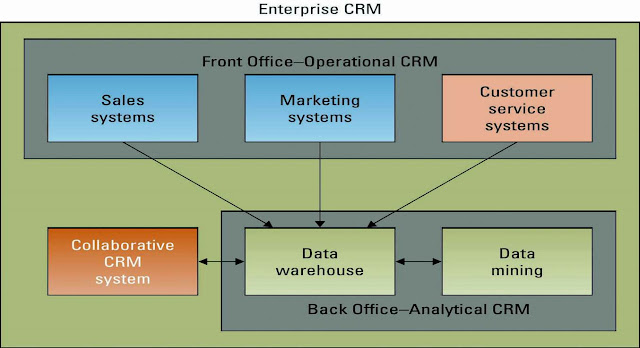
-
Operational
CRM – supports traditional transactional processing for day-to-day
front-office operations or systems that deal directly with the customers
-
Analytical
CRM – supports back-office operations and strategic analysis and
includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers
-
Operational CRM and analytical CRM
Customer
Relationship Management Success Factors
CRM success
factors include:
·
Clearly
communicate the CRM strategy
·
Define
information needs and flows
·
Build
an integrated view of the customer
·
Implement
in iterations
·
Scalability
for organizational growth



Comments
Post a Comment